Simply said, edge banding addresses an issue in the furniture manufacturing process.
The issue is that when hardwood boards are cut, they contain a rough edge that, if left exposed, may cause severe issues for your furniture.
Raw edges are not only unsightly, but they also allow moisture to seep in, causing the wood to warp and, as a result, significantly reducing the wood’s life span.
It is also very detrimental to one’s looks.
Edge banding is the thin strips that cover the ends of raw wood boards.
Edge banding protects your furniture’s hardwood panels from moisture, minimizing the impacts of ambient humidity and liquid spills.
Just like the purpose of furniture covers such as pet furniture covers, edge banding serves as a protective guard that secures the edges of your furniture and prevents detrimental accidents.
If you are curious to know more about edge banding, in this article, we will thoroughly discuss the different types of edge banding and their purpose.

1. The Purpose of Edge Banding
3. How To Put an Edge Banding?
1. The Purpose of Edge Banding

Edge banding is a thin layer used to cover the uncovered and raw borders of plywood.
On one side, heat-sensitive glue is placed on the board, while the other side serves as a shield against dust and moisture.
Edge banding is used to wrap plywood sides to match the final appearance of a cabinet, but it also prevents the interior plywood from warping.
Edge banding is used for both practical and aesthetic reasons.
Edge bands provide important functions for your furniture.
For starters, it keeps moisture out by acting as a de facto seal on the core material’s edge. Second, by offering impact resistance, edge banding increases durability and resilience.
If you choose solid wood edging, it may also help to strengthen the overall robustness of the furniture.
Edge banding hides undesirable rough edges and provides a glossy finish that matches your tops and sides. Radial edges may also be used to soften acute angles.
2. Types of Edge Banding

2-1. Wood Veneer Edgebanding
Another popular edge banding material is wood veneer.
Wood veneer edgebanding is made by finger-jointing separate pieces of veneer into a seamless master roll.
Veneer means “thin pieces of wood”.
Common types include walnut, mahogany, maple, ash, and oak, but there are many more, including natural and colored veneers!
The attractiveness, durability, and strength of wood veneer are amongst the strong advantages of getting a wood veneer for your furniture.
It has a clean solid-wood appearance and is pre-sanded to readily absorb staining and finishes to match your wood.
However, wood veneer products are not heat resistant. Avoid placing it near a heater. It does not perform well in extreme environments.
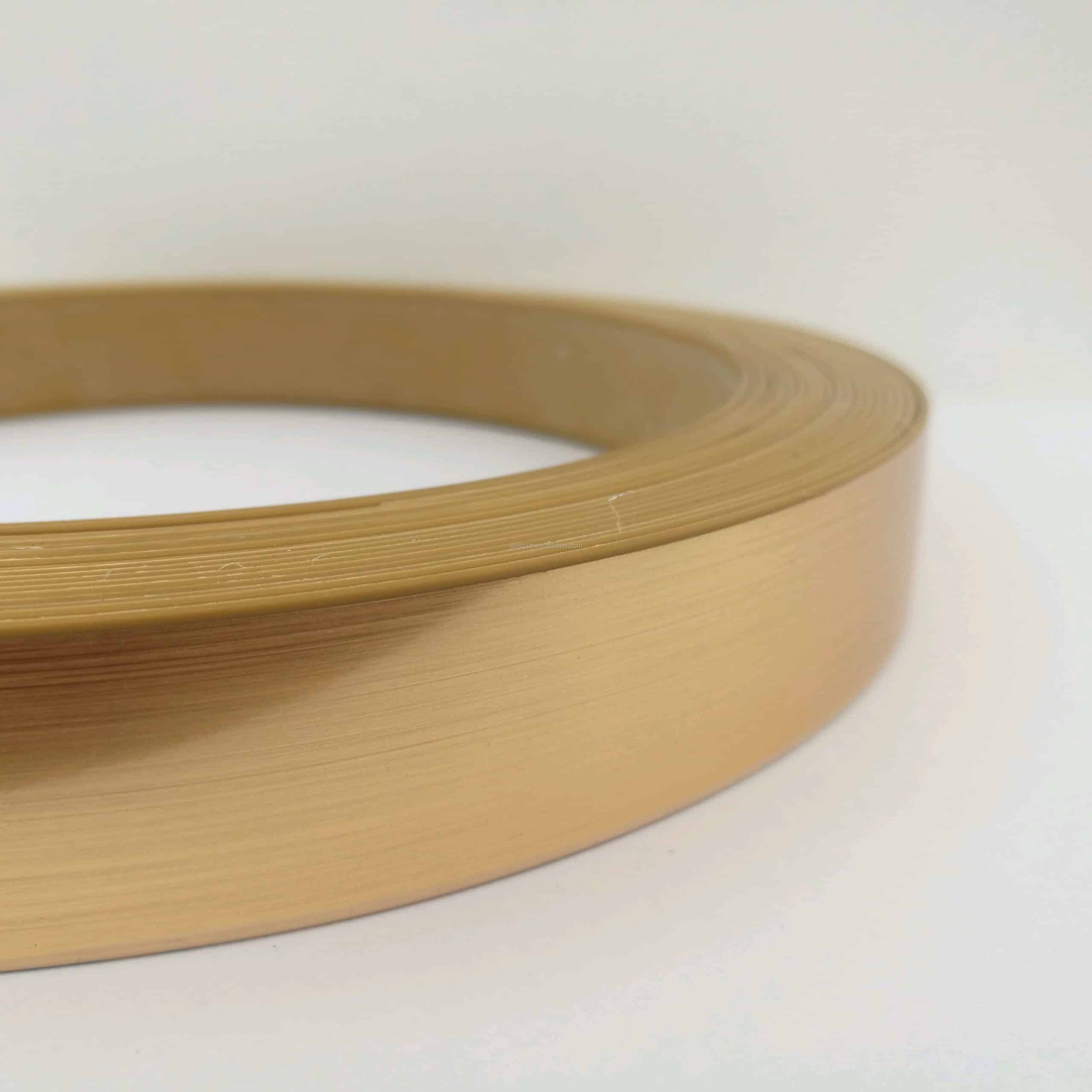
2-2. PVC
PVC is the most often used edge banding material.
Because of its outstanding processing properties, it is the most frequently utilized in the production of edge bands for the furniture sector.
PVC edge banding is particularly popular for modular furniture since it is very robust, easy to repair, and has an exceptionally long life.
It does not require any kind of finishing procedure. It is also simple, though time-consuming, to fix.
However, PVCs cannot be recycled. You can’t refinish it after it’s tarnished.
When it comes to PVC, we often prefer 3mm edging since it goes on cleaner, faster, and with greater adherence.
Another benefit is that you get a beautiful soft-looking finish and a graceful radius.
In general, we try to avoid 5mm edging since the edges have the tendency to be sharp.
2-3. PP (Polypropylene)

Polypropylene is used to make PP edgebanding. Polypropylene is one of several thermoplastic polymers available on the market.
Among plastic edge banding options, PP edge banding is the most environmentally friendly, flexible, and heat resistant. Comparing it to plastic furniture covers, polypropylene can endure extreme conditions.
PP edgebanding is an excellent option for narrow radius applications and areas where furniture is subjected to high temperatures and heat.
PP is a semi-crystalline plastic that is widely utilized in the packaging sector.
It is ideal for small radius applications, is chlorine-free, and is widely utilized as an alternative to conventional PVC and ABS materials in the furniture sector.
2-4. ABS
ABS is a high-quality thermoplastic that is very resistant to common knocks and scratches, making it ideal for high-traffic furniture.
It can tolerate water, is very heat resistant, and is unaffected by household cleaning agents, making it ideal for family kitchens.
It’s also an excellent choice for usage in offices, toilets, all interior furnishings, store fitting, coffin making, and even exhibition displays.
Because of its excellent heat resistance, it may be used on kitchen cabinets close to hot ovens or stoves without causing damage or distortion.
ABS is a versatile edging material with almost limitless application possibilities.
You may mold this material to suit your design style, whether straight edge boards, curves, or unique forms. It’s also simple to work with on-edge banding devices.
ABS is less dense and lighter in composition than PVC, yet it still offers a very robust surface to protect your board edges.
It has some of the same advantages as PVC, but it is also completely recyclable and biodegradable.
2-5. Laser Edgebanding or Zero-Joint Edgebanding
A pre-applied, co-extruded polymer functional layer attaches to the board without the need for glue in zero-joint edgebanding.
The functioning layer dissolves and fuses the edge band to the board when activated by a laser, hot air, or NIR edge bander.
In contrast to glue adhesive techniques, zero-joint applications only need the joining of two items: the edge band and the board.
Regardless of its simplicity, zero-joint edge banding is a sophisticated adhesion technique that provides many significant advantages.
Zero-joint edgebanding enables the wood and the edge band to look like one solid surface, adding to the polished aspect of meticulously designed spaces inside the house.
Zero-joint edgebanding creates a monolithic look by making the board and edge band seem to be one solid surface.
Zero-joint edgebanding not only eliminates the need for glue pot maintenance but also eliminates splatter or glue problems within edge banders.
Working with glue slows the production process, necessitating pre-heating and closing down, and may result in operator burns, all of which can be avoided using zero-joint edgebanding.
3. How To Put an Edge Banding?
An edge band is just a thin strip of waterproof PVC trimmed to suit the dimension of a wood panel.
The rough edge is then adhered to using a strong adhesive.
The adhesive is then melted and the edge band is glued over the wood using a heat roller.
The ends are cut flat and curved to hide the wood and avoid any rough edges.
Any excess glue is scraped away, and the final edge is polished to a perfect shine.
An edge bander is a machine that is utilized for this procedure.
4. Takeaways
We hope we were able to shed a light on the edge banding, its different types, and its purpose.
There are different types of edge banding that can be utilized for various situations. There are many edge bands on the market, ranging from pre-glued to 3D acrylic adhesives.
The ideal one for your furniture is determined by the material it is composed of.





0 Comments